What is ELISA Mechanism?
ELISA (Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay)
The Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA) (NCBI) is one of the most widely used analytical techniques in modern laboratories for detecting and quantifying proteins, peptides, antibodies, and other biomolecules. ELISA works through a highly specific antibody–antigen interaction, allowing researchers to measure target analytes with accuracy, sensitivity, and reproducibility. Because the method uses enzyme-driven signal generation, it provides clear, quantifiable results suitable for routine testing, research workflows, and high-throughput screening.
Built on simple microplate-based steps "coating, binding, washing, and detection" ELISA offers a predictable workflow that can be adapted for many experimental designs. Whether used for cytokine analysis, protein measurement, biomarker monitoring, or general immunoassay applications, ELISA remains a fundamental tool for laboratories needing a reliable method to measure biological molecules across a wide range of sample types.
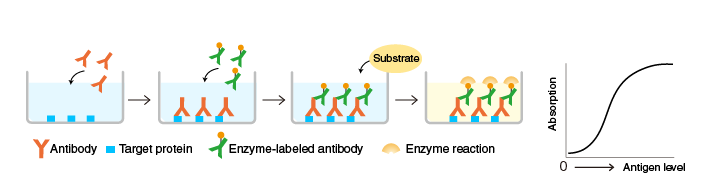
Performing an ELISA involves at least one antibody with specificity for a particular antigen. The sample with an unknown amount of antigen is immobilized on a solid support (usually a polystyrene microtiter plate.
see in detail in the section of ELISA device) either non-specifically (via adsorption to the surface) or specifically (via capture by another antibody specific to the same antigen, in a "sandwich" ELISA). After the antigen is immobilized, the detection antibody is added, forming a complex with the antigen.
The detection antibody can be covalently linked to an enzyme, or can itself be detected by a secondary antibody that is linked to an enzyme through bioconjugation. The part of antibody incubation of ELISA is similar with that of western blot.
Between each step, the plate is typically washed with a mild detergent solution to remove any proteins or antibodies that are not specifically bound. After the final wash step, the plate is developed by adding an enzymatic substrate to produce a visible signal, which indicates the quantity of antigen in the sample.
Why Understanding the ELISA Mechanism Matters in Modern Laboratory Research
The ELISA mechanism is more than a standard immunoassay, it's a core analytical technique used across life-science research, biotechnology, molecular biology, and quality control laboratories. Understanding how ELISA works allows researchers to achieve higher sensitivity, better reproducibility, and more confident analyte detection across a wide range of samples.
Today, ELISA technology is applied in:
- Protein quantification and biomarker discovery.
- Cytokine, chemokine, and growth-factor detection.
- Antibody-antigen interaction studies.
- Cell culture analysis.
- Purity testing and biological product evaluation.
- Food and environmental monitoring.
This makes ELISA an essential tool for academic research, biotech companies, CROs, and industrial laboratories where reliable immunoassay performance is critical.
Key Factors That Influence ELISA Accuracy and Reliability
To ensure the ELISA mechanism works optimally, several parameters must be carefully controlled:
1. Plate Quality and Coating Efficiency
High-binding microplates improve antigen capture and increase assay sensitivity. Proper coating ensures uniform antibody immobilization across the well surface.
2. Antibody Affinity and Specificity
Well-validated primary and secondary antibodies reduce background noise and improve the signal-to-noise ratio-one of the most important factors in ELISA performance.
3. Incubation Time and Temperature
The kinetics of antigen-antibody interactions depend on consistent temperature and optimized incubation periods, ensuring reliable and repeatable detection.
4. Washing Efficiency
Insufficient washing is one of the top causes of inconsistent ELISA results. Proper wash buffers remove unbound components and increase signal clarity.
5. Substrate Reaction & Signal Measurement
Chromogenic, fluorescent, or chemiluminescent substrates provide different levels of sensitivity. Understanding the detection system is essential for correct quantification.
Types of ELISA Formats Used in Today’s Laboratories
To complement your current content, here is a clear, human-friendly explanation of each major ELISA type tuned for SEO performance:
✔ Direct ELISA
Fast and simple, ideal for detecting antibodies or antigens with minimal washing steps.
✔ Indirect ELISA
Enhances sensitivity by using a labeled secondary antibody. Preferred for antibody detection.
✔ Sandwich ELISA
The most specific and sensitive format; captures the target antigen between two matched antibodies.
✔ Competitive ELISA
Suitable for small molecules, peptides, and analytes present at low concentrations.

