ELISA Kits
There are five types of ELISA, so about ELISA protocol, some differences exist between indirect ELISA protocol, direct ELISA protocol, sandwich ELISA protocol, competitive ELISA protocol and ELISPOT protocol. However, the main ELISA principle and many procedures are the same. The general ELISA protocol includes the preparation of the plates, the assay procedure and the calculation of the results.
(ELISA protocol) Plate preparation
1. Dilute capture antibody to working concentration in CBS. Immediately coat a 96-well microplate with 100 μL per well of the diluted capture antibody. Seal the plate and incubate overnight at 4℃.
2.Aspirate each well and wash with at least 300μL of Wash Buffer, repeating the process twice for a total of three washes. Complete removal of fluid at each stage is essential for good performance. After the last wash, remove any remaining wash buffer by inverting the plate and dabbing it against clean paper towels.
3. Block the plates by adding 300 μL of blocking buffer to each well. Incubate at room temperature for at least 1 hour.
4.Repeat aspirate/wash as in step 2. Plates are now ready for sample addition.
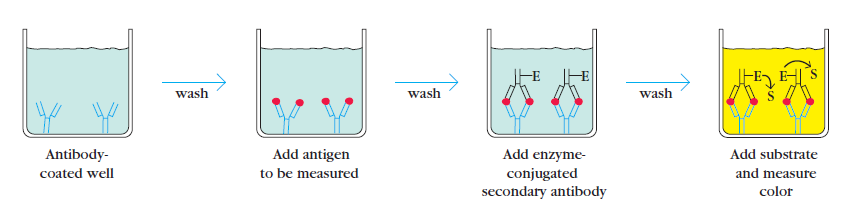
(ELISA protocol) Assay procedure
1.Add 100μL of sample or standards in Sample Dilution Buffer per well. Seal the plate and incubate for 2 hours at room temperature.
2.Repeat aspirating/washing as in step 2 of plate preparation.
3.Add 100μL of detection antibody, diluted in antibody dilution buffer, to each well. Seal the plate and incubate for 1 hour at room temperature.
4.Repeat aspirate/wash as in step 2 of plate preparation.
5.Add 200μL of Substrate Solution to each well. Incubate for 20 minutes at room temperature (if the substrate solution is not the one requested, the incubation time must be optimized). Avoid placing the plate in direct light.
6.Add 50μL of Stop Solution to each well. Gently tap the plate to ensure thorough mixing.
7. Immediately determine the optical density of each well using a microplate reader set to 450 nm.

(ELISA protocol) Calculation of results
1.Calculate the average absorbance for each set of standards, controls, and duplicate samples. Subtract the mean zero standard absorbance from each.
2. Construct a standard curve by plotting the mean absorbance for each standard on the y-axis against the concentration on the x-axis and plot a curve of best fit through the points on the graph.
3. To determine the concentration of the unknowns, find the mean absorbance value of the unknowns on the y-axis and draw a horizontal line to the standard curve. At the point of intersection, draw a vertical line to the x-axis and read the concentration. If the samples have been diluted, the concentration read on the standard curve must be multiplied by the dilution factor.
4. Alternatively, computerized curve-fitting statistical software can also be used to calculate the sample concentration.